 CN / EN
CN / EN
Shanghai University of Engineering Science
CHINGMU Research | The Impact of Fabric Elastic Modulus on the Shock-Absorption Performance of Sport
Client: Professor Chen Xiaona’s Team, College of Textiles and Fashion, Shanghai University of Engineering Science
Paper: Quantitative Relationship Between Fabric Elasticity and Shock Absorption Performance of Sports Bras
Applications: Motion Capture, Soft Body Tracking, Position Measurement, Shock Absorption Performance of Sports Bras
Shock-Absorption in Sports Bras

Due to the lack of muscle and skeletal support, the primary source of structural support for the female breast comes from the Cooper’s ligaments, supplemented by the superficial fascia and skin. During physical activity, external support is crucial to lift the breasts into a position where internal structures experience minimal stress, reducing discomfort caused by vibrations and preventing potential sagging or other breast health issues. This is the fundamental purpose of shock-absorption in sports bras.
Research indicates that the mechanism of shock-absorption in sports bras should focus on the interaction between the breasts and the bra. Future studies should delve into fabric and structural parameters to quantify their relationship with breast displacement, enabling optimized shock-absorption designs for sports bras.

Against this background, Associate Professor Chen Xiaona from Shanghai University of Engineering Science led a team, including Sheng Xinyang, to conduct research on how fabric elastic modulus affects the shock-absorption performance of sports bras. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation and the Key Laboratory of Modern Garment Design and Technology at Donghua University.
The research team utilized CHINGMU’s proprietary MC Optical Motion Capture (MC-MoCap) system to overcome experimental constraints. This solution significantly reduced research costs while enhancing the precision of experimental data collection, ensuring the smooth progression of their study.
Experimental Setup
Eight participants were asked to wear two sets of sports bras with identical designs but differing fabric compositions:
•Sample 1: Fabric containing 30% spandex
•Sample 2: Fabric containing 20% spandex
Participants performed jump rope exercises without a rope at a frequency of 2 Hz. The team recorded breast displacement during the exercise and collected subjective comfort ratings from the participants.
The upper body of each participant was marked at five key points:
1.M1: Suprasternal notch of the manubrium.
2.M2 and M3: Left and right nipple points.
3.M4 and M5: At the 10th rib on both sides, aligned with the nipples.
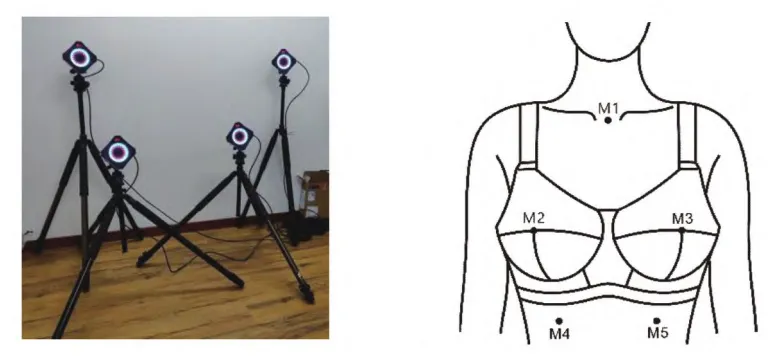
A thoracic coordinate system was established using M1, M4, and M5 as reference points, with M2 and M3 representing the left and right breasts, respectively. Using four CHINGMU MC optical motion capture cameras, the researchers tracked marker positions in the lab’s global coordinate system and converted them to the thoracic coordinate system for relative displacement calculations. Since the torso primarily moves vertically during jump rope, this study focused on vertical breast displacement.
MC Optical Motion Capture Solution
CHINGMU provided both passive and active optical motion capture solutions from its MC series. For the study, active optical capture was employed due to its ability to maintain consistent marker IDs, ensuring accurate positional data for soft tissues during motion.
CHINGMU’s R&D team developed several customized software functions tailored to the experiment’s needs. These functions, including marker data in TRC format, streamlined data collection, simplified workflows, and improved both efficiency and accuracy.
Prior to using CHINGMU’s system, the research team attempted experiments with 12 cameras from an international brand, but the high costs and suboptimal data resolution failed to meet their needs. CHINGMU’s MC series system, utilizing just four cameras, provided an economical and efficient solution, enabling the team to complete the project within a tight schedule.

CHINGMU MC Series Optical Motion Capture System
Experimental Results
During the 2 Hz jump rope exercise, the average vertical breast displacement was:
•Sample 1 (30% spandex): 15.8 mm
•Sample 2 (20% spandex): 16.7 mm
Similarly, subjective discomfort scores were:
•Sample 1: 1.17
•Sample 2: 1.00
Both metrics indicate that Sample 1 (with higher spandex content) exhibited better shock-absorption performance. The results showed that as the elastic modulus of the fabric increased, breast displacement and discomfort decreased, highlighting the direct relationship between fabric properties and the effectiveness of sports bras.
The Role of Motion Capture
CHINGMU’s MC series optical motion capture system enabled the research team to use objective evaluation methods to track and record breast and torso movement trajectories. This system provided precise, repeatable data visualization, revealing the shock-absorption performance of the sports bras. The optical motion capture technology ensured that experimental results were presented in a clear, data-driven format, offering enhanced reliability and reproducibility.
By integrating advanced motion capture systems, CHINGMU continues to support cutting-edge research in biomechanics, providing tailored solutions that address specific experimental challenges and deliver impactful insights.
Key Takeaway
CHINGMU’s MC series has proven to be a cost-effective and high-precision alternative to traditional motion capture systems, enabling researchers to innovate in fields such as biomechanics and sports apparel development.