 CN / EN
CN / EN
How Motion Capture Drives Digital Humans


Motion capture (MoCap) technology is widely used in the production of virtual idols, virtual hosts, virtual singers, cultural and tourism figures, brand ambassadors, and more. Through MoCap-based applications, the presentation of digital humans becomes more realistic and natural, delivering a highly immersive interactive experience. So, how does motion capture drive digital humans? This process can be broken down into three steps: capturing MoCap data from real humans, constructing a digital human model, and generating the digital human image.
1. Capturing MoCap Data from Real Humans
The realism of a digital human—its body movements and facial expressions—is largely achieved by capturing data from a real person. This requires specialized equipment such as MoCap cameras and facial capture helmets.
1.1 Facial Capture
By using a MoCap helmet, facial expressions are accurately replicated, capturing every subtle movement from a frown to a smile.
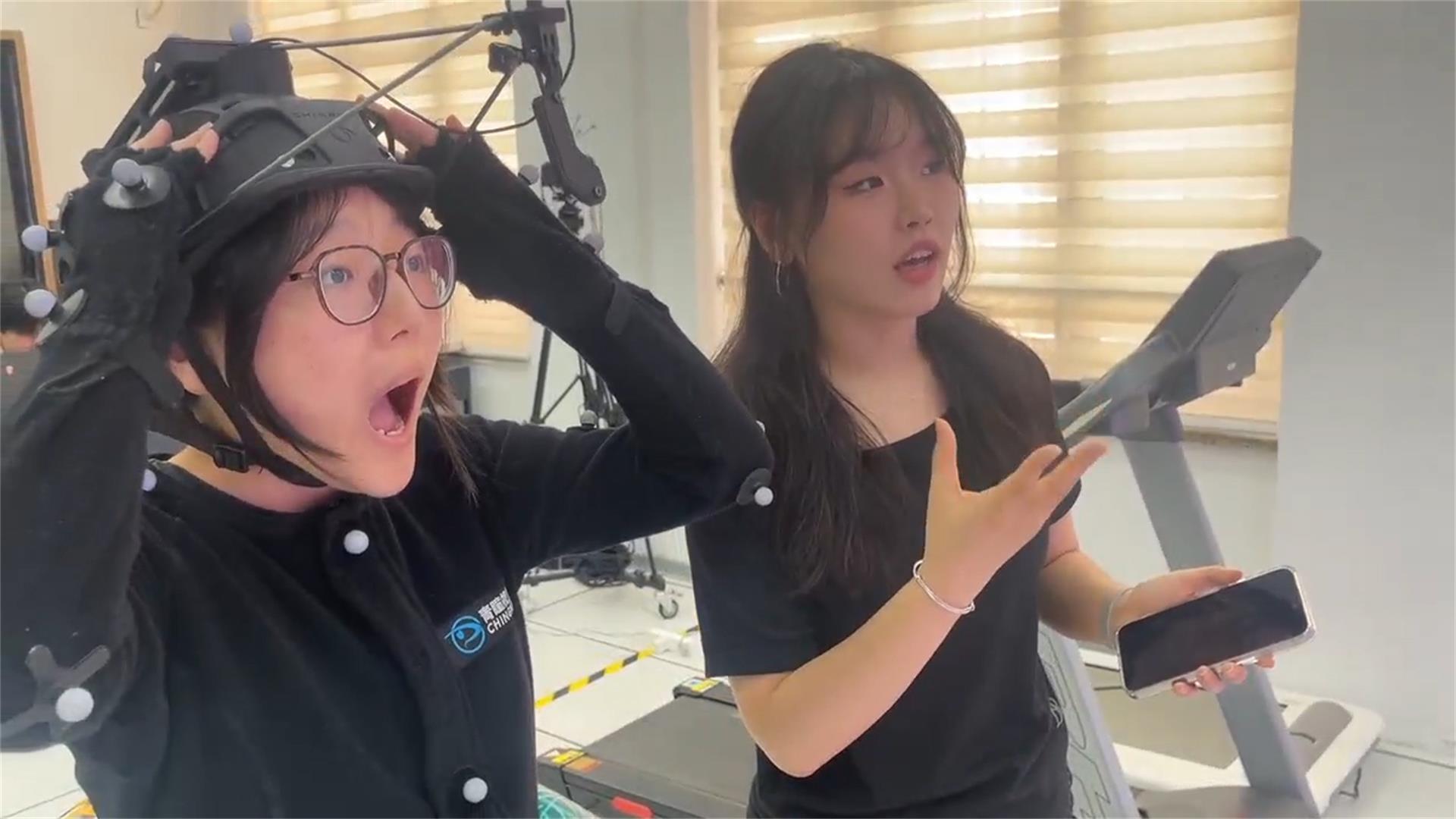

1.2 Full-body Capture
In a MoCap-equipped environment, such as a MoCap studio, performers wear a MoCap suit while performing. MoCap cameras track the markers on the suit, capturing real-time data related to the body’s movement in three-dimensional space, including movement trajectories, positioning, and body actions.
2. Constructing the Digital Human Model
The data collected by MoCap cameras is transmitted in real-time to MoCap software, where it is used to construct a digital skeleton. This model reflects the joints, limbs, and overall body structure of the real person, based on the captured movement data.

3. Generating the Digital Human Image
Once the digital human model is built, the MoCap data of the human skeleton is integrated with the 3D digital human model. This results in real-time animation, where the movements of the digital human are precisely rendered, achieving synchronous performance and one-to-one motion representation.
CHINGMU provides comprehensive technical support and services in digital human modeling, motion capture, content creation, and multi-scenario interaction. Their solutions are widely applied in industries such as cultural tourism, TV broadcasting, live streaming, virtual idols, and personal branding, earning broad recognition from clients. Notable projects include million-level virtual idols like Jinju and Huli Li, the Liu Sanjie digital human for Guangxi Cultural Tourism, YAOYAO, a virtual human for Hunan Broadcasting, Xiao Ya, the digital human reporter for Zhejiang, and Nai Si, the digital human for Mengniu. Additionally, CHINGMU supported major events such as the Virtual Fes 2023 Hong Kong VTuber 3D concert, the Tingchao Pavilion virtual music show, and the Tu Mian Keke one-year anniversary 3D live event.